Thrips
There are several species of thrips that feed on cannabis. In cannabis production, the most common is the Western Flower Thrips, Frankliniella occidentalis. However, other similar thrips species like onion thrips and even Echinothrips have been found by cultivators. We will focus on the Western Flower thrips in this section.
-
 Swirski-Mite Ulti-Mite Sachets
Swirski-Mite Ulti-Mite SachetsSwirski-Mite Ulti-Mite Sachets (Amblyseius swirskii) — Predatory Mite for Thrips, Whiteflies &…
Use For Thrips, White Fly, Broad and Russet Mites, Two-Spotted Spider Mites, Flat MitesSpecies A. swirskii$34.28 -
 Entomite-M
Entomite-MEntomite-M (Stratiolaelaps scimitus) — Soil-Dwelling Predator for Fungus Gnats & Thrips Pu…
Use For Thrips, Root Aphids, Fungus GnatsSpecies S. scimitus/H. miles$21.42 -
 Entonem (OMRI)
Entonem (OMRI)Entonem (OMRI) — Steinernema feltiae - Nematodes for Soil and Foliar Pest Control Entonem cont…
Use For Fungus Gnats, Thrips, Beetles, CaterpillarsSpecies S. feltiae$38.29 -
 Thripor
ThriporThripor (Orius insidiosus) — Predatory Bug for Thrips ControlThripor contains Orius insidiosus…
Use For Thrips, Two-Spotted Spider MiteSpecies Orius insidiousus$136.48 -
 Swirski-Mite
Swirski-MiteSwirski-Mite (Amblyseius swirskii) — Predatory Mite for Thrips, Whiteflies & Pest MitesSwi…
Use For Thrips, White Fly, Broad and Russet Mites, Two-Spotted Spider Mites, Flat MitesSpecies A. swirskii$147.83 -
 Swirski-Mite PLUS Sachets
Swirski-Mite PLUS SachetsSwirskii-Mite PLUS Sachets (Amblyseius swirskii) — Predatory Mite for Thrips, Whiteflies &…
Use For Thrips, White Fly, Broad and Russet Mites, Two-Spotted Spider Mites, Flat MitesSpecies A. swirskii$80.34 -
 Thripex
ThripexThripex Bottles (Neoseiulus cucumeris) — Predatory Mite for Thrips and Mite ControlThripex bot…
Use For ThripsSpecies N. cucumeris$32.14 -
 Horiver Sticky Traps
Horiver Sticky TrapsHoriver Yellow Sticky Traps — 10-Pack (3.94" x 9.84") Monitoring & Trapping for Flying Ins…
Use For Aphids, Leaf Miners, Whiteflies, Thrips, Sciarids$10.18 -
 Thripex-V
Thripex-VThripex-V Bottles (Neoseiulus cucumeris) — Predatory Mite for Thrips and Mite ControlThripex-V…
Use For Thrips, Mite Spp.Species N. cucumeris$38.56 -
 Thripex PLUS
Thripex PLUSThripex Plus Sachets (Neoseiulus cucumeris) — Predatory Mite for Thrips and Mite ControlThripe…
Use For ThripsSpecies N. cucumeris$139.26 -
 Isarid Mycoinsectide
Isarid MycoinsectideGeneral information When to use Isarid? Isarid™ works best in a pest management program de…
Use For whiteflies, aphids, thrips, psyllids, mealybugs, leaf hoppers, plant bugs*, weevils*, grasshoppers*, Mormon crickets, locust, beetles, mites, bagrada bugs, lygus bugs, and fungus gnats*. *Not Registered for Use By California$220.67 -
 Thripex-Mini (w/stake)
Thripex-Mini (w/stake)Thripex-Mini Sachets with Sticks (Neoseiulus cucumeris) — Predatory Mite for Thrips and Mite C…
Use For Thrips, Mite Spp.Species N. cucumeris$117.83
More Information about Thrips
[↑ Back to Top]With their small size, hyper-reproductive capacity, and resistance to common pesticides, the western flower thrips has become increasingly hard to control in agriculture and horticulture. Thrips feed on plant material, but their reproduction and activity is kicked into overdrive by the presence of pollen. The lack of pollen in female cannabis has shown to limit the activity of western flower thrips to a degree (thankfully so).
Despite the lack of pollen, thrips can still cause major leaf and stem damage, and they are a difficult pest to manage. Their complicated life history occurs inside plant tissue, in the soil, and on the plant's surface. Once mature, thrips adults can live for 30 days, or more. To gain the upper hand on this pest, patience and a ‘systems approach’ is often required.
What to Look For
- Adult thrips are about 1/16th of an inch long. Adults are long, slender winged insects, that can resemble grass seed to the naked eye.
- Adults have two sets of narrow, clear, nearly veinless wings that have dark, hairy fringes.
- Females can range in color from amber, or yellowish-brown, to dark brown. Males are similar to females but smaller and always light yellow.
- Larvae resemble adults, but are wingless.
- A female will lay 150-300 eggs in her lifetime. Eggs are delicate, cylindrical, slightly kidney-shaped, smooth and translucent white, which are inserted into plant tissue, making them very difficult to detect, and also protects them from many contact-dependent insecticides.
Damage/Symptoms
Thrips can causesignificant damage through their feeding behaviors, piercing the plant cells and sucking out their contents with their mouth parts and feeding on the sap that seeps from the wounds.
Puncturing the plant with its single mandiblealso makes them a primary vector for transmitting various diseases, such as tospoviruses.
Winged adult thrips are primarily responsible for spreading viruses, and an infected thrips is able to transmit tospoviruses to at least one plant per day until its death (~30 days).
Symptoms of damaged plant cells that collapse include: deformed foliage and flowers, and/or silvered patches and flecking on expanded leaves.
Damaged leaves may appear puckered and/or twisted. Feeding on plant tissue forms pale spots as the thrips slash the surface of the leaf and suck out the contents of the cells beneath.
Thrips oftentimes leave specks of black feces on the surface/underside of leaves, so be sure to look on the undersides of leaves for the fast moving larvae and fecal matter, or tap branches of the plant onto a sheet of white paper and look for any thrips that are dislodged.
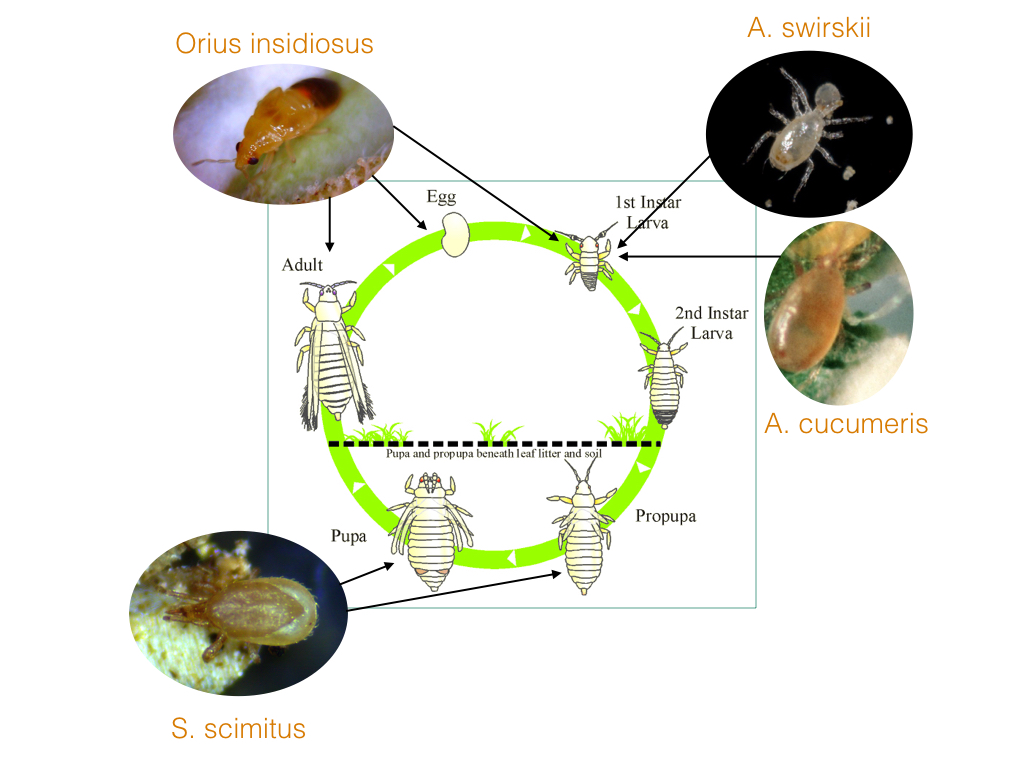
Thrip Life Cycle
Western flower thrips have 6 life stages. The larval and adult stages actively feed on plants.
Egg- Thrips eggs are deposited into plant stems, petioles, and leaves by females using a saw-like ovipositor.
Duration- 2 to 4 days
Larval instar 1- Thrips larvae do not have wings when they emerge, but are able to feed on the plant.
Duration:
Larval instar 2- The second larval instar is larger than the first, feeding on the plant before entering the pupal stage.
Duration:
Pro-, and pupa stage- The larva normally drop to the soil to pupate. However, they can pupate on the host plant in ‘complex floral architecture’. The pupal stages do not feed.
Duration: 1 to 3 days
Adult- Winged adults emerge after pupation, ready to feed and looking to oviposit eggs.
Duration: Over 30 days, depending on environment.
Biology
- Western Flower Thrips (WFT) develop between 47 and 95˚F
- Under optimal conditions of 77 to 86˚F, WFT can go from egg to adult in 9 to 13 days.
- Thrips are well known vectors of tospoviruses, including Impatiens Necrotic Spot Virus and Tomato Spotted Wilt Virus.
- Larval instars 1 & 2 are the only life stages that can contract a virus from a host plant. The second larval instar, along with the adults, are capable of spreading any virus that is acquired.
- Adults must feed for 5 minutes in order to transmit any virus they may be carrying. It takes about 30 minutes for the lavae to acquire the virus.
- The mouthparts are ‘rasping/sucking’, meaning the thrips scrape the leave surface to damage it, and then suck the plant juices.
- Greenhouse populations of WFT are not sensitive to short days, and will not undergo diapause.
- While capable of flight, WFT adults are poor fliers. They can, however, travel far distances being carried by the wind, or by hitching a ride in, or on, plants, so be sure to properly inspect all incoming plants/clones/cuttings.
Additional Notes
-Thrips larvae will defend themselves against predatory mites, with the 2nd larval instar being especially difficult for the mites to handle. The larvae will whip their abdomens at the mites, often spraying them at the same time.
I see thrips, now what?
Due to the complexity of the WFT life-cycle, there are multiple predators that will have an impact against one or more of these phases. As such, the most effective strategy against these pests will be toincorporatemultiple predators in order tointerrupt the lifecycle in as many ways as possible. The above diagram will give you an idea of which predators will be effective against the various phases, though a combination of Orius, swirskii, and soil mites has been the most effective in controlling these pests. However, there are other factors at play that will affect whichpredator you choose, such as previous/recent chemical interventions, current phase of thegrowth cycle, and growing media. If you have questions, please feel free to fill out our Commercial Cultivation Inquiry for guidance tailored to your unique situation.
I don't see any, but I want to prevent problems...
The primary differences between a curative and preventative approach for thrips would be in the packaging/container type you choose and the intervals of re-application. For a preventative program geared toward WFT, the slow-release sachets of cucumeris or swirskii will provide a primary line of defense in your canopy against the 1st and 2nd larval instar stages of the thrips life-cycle. In addition, as there is no pollen in cannabis plants to sustain the populations of Orius when pest populations are low, the use of banker plants, such as Purple Flash ornamental peppers, have been used effectively to provide a stable food source for the Orius.

