Lions, Tigers, and Bugs, Oh My!
Mar 25, 2025
When we think of lions and tigers, our minds often wander to the majestic creatures of the savannah and the dense jungles. However, in the world of gardening and agriculture, there are other "lions" and "tigers" that play a crucial role in maintaining the health of our plants. These are the Aphid Lions and Mealybug Destroyers, two formidable allies in the battle against pests.
Imagine a garden teeming with life, where every plant thrives and every problem is kept in check by nature's own guardians. Aphid Lions, also known as Green Lacewing larvae, and Mealybug Destroyers, scientifically known as Cryptolaemus montrouzieri, are two heroes of this vibrant ecosystem. These beneficial insects are not just ordinary bugs; they are fierce predators that help maintain the delicate balance of our plants, gardens and agricultural fields.
In this article, we will delve into the fascinating world of these beneficial insects, exploring their biology, behavior, and the vital role they play in integrated pest management. From their life cycles and hunting techniques to their adaptability and effectiveness in various environments, we will learn more about these tiny natural predators. By understanding how Aphid Lions and Mealybug Destroyers operate, we can harness their power to create more sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions for our plants.
Join us as we embark on a journey into the world of Aphid Lions and Mealybug Destroyers, and discover how these tiny predators can make a big difference to you. Whether you're experienced or just starting out, learning more about beneficial insects will equip you with the knowledge to protect your plants. So, let's dive in and explore the incredible world of beneficial insects and their role in keeping our ecosystems in balance.
The Mighty Aphid Lions (Learn More)
Aphid Lions, also known as Green Lacewing larvae, are voracious predators of aphids, one of the most common and destructive problems in gardens and agricultural fields. The adult Green Lacewing is a delicate, green insect with large, transparent wings. However, it is the larval stage that earns the name "Aphid Lion" due to its fierce predatory nature.
Biology and Life Cycle
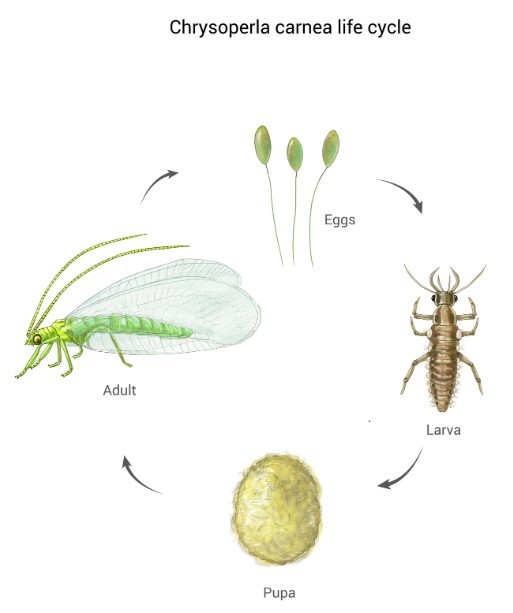
The life cycle of the Green Lacewing begins with the female laying eggs on the underside of leaves. These eggs are often laid on slender stalks, which help protect them from predators. Once the eggs hatch, the larvae emerge, ready to hunt. Aphid Lions are equipped with powerful mandibles that they use to pierce their prey and inject digestive enzymes. These enzymes liquefy the internal contents of the aphid, which the larvae then suck up, leaving behind an empty husk.
The larval stage lasts for about two to three weeks, during which an Aphid Lion can consume hundreds of aphids. After this period, the larvae pupate, forming a cocoon in which they undergo metamorphosis. Within a week or two, the adult Green Lacewing emerges, ready to continue the cycle.
Behavior and Hunting Techniques
Aphid Lions are highly effective hunters, using both their keen sense of smell and sight to locate their prey. They are particularly attracted to the honeydew secreted by aphids, which serves as a beacon, guiding them to their next meal. Once an Aphid Lion locates a colony of aphids, it methodically hunts them down, one by one.
In addition to aphids, Aphid Lions also prey on other soft-bodied insects such as mealybugs, whiteflies, and spider mites. This makes them a valuable asset in integrated pest management programs, as they help control multiple pest species simultaneously.
The Fearsome Mealybug Destroyers (Learn More)
Mealybug Destroyers, scientifically known as Cryptolaemus montrouzieri, are another group of beneficial insects that play a crucial role. These beetles are native to Australia but have been introduced to various parts of the world as a biological control agent against mealybugs.
Biology and Life Cycle
The life cycle of the Mealybug Destroyer begins with the female laying eggs among the egg sacs of mealybugs. The eggs hatch into larvae that closely resemble their prey, covered in white, waxy filaments. This mimicry helps protect the larvae from potential predators.
Like Aphid Lions, Mealybug Destroyer larvae are voracious predators. They feed on mealybug eggs, nymphs, and even adult mealybugs. The larvae go through several instars, or growth stages, before pupating. The pupal stage lasts for about a week, after which the adult beetle emerges.
Adult Mealybug Destroyers are small, dark brown beetles with a distinctive orange head and thorax. They continue to feed on mealybugs, but their primary role is reproduction, ensuring the next generation of predators.
Behavior and Hunting Techniques
Mealybug Destroyers are highly effective at locating and eliminating mealybug infestations. They are particularly attracted to the honeydew secreted by mealybugs, which serves as a food source for both the larvae and adults. The larvae use their powerful mandibles to pierce the mealybugs and suck out their internal contents, much like Aphid Lions.
One of the unique aspects of Mealybug Destroyers is their ability to adapt to different environments. They can thrive in both indoor and outdoor settings, making them a versatile tool. Additionally, as adults they are highly mobile, capable of covering large areas in search of prey.
The Role of Beneficial Insects in Integrated Pest Management
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is an environmentally friendly approach that combines biological, cultural, physical, and chemical methods to manage pest populations. Beneficial insects like Aphid Lions and Mealybug Destroyers play a crucial role in IPM by providing natural, sustainable control.
Advantages of Using Beneficial Insects
Unlike chemical pesticides, beneficial insects do not pose a risk to the environment or human health. They target specific pests, leaving non-target organisms unharmed. Beneficial insects provide long-term pest control by establishing populations that can persist and reproduce in the environment. By relying on natural predators, growers can reduce their reliance on chemical pesticides, leading to lower pesticide residues on crops and reduced risk of pesticide resistance.
To effectively use beneficial insects in IPM, it is essential to create a conducive environment for their survival and reproduction. This includes avoiding the use of broad-spectrum pesticides that can harm beneficial insects.
To learn more about what to avoid and what to use, check out our compatability pages here.
Monitoring problem populations is also crucial to determine the appropriate timing and quantity of beneficial insect releases.
The Unsung Heroes
Aphid Lions and Mealybug Destroyers are two remarkable examples of beneficial insects that play a vital role in maintaining the health of our plants. Their predatory nature and ability to control multiple pest species make them invaluable allies in integrated pest management. By understanding their biology, behavior, and the benefits they provide, we can harness the power of these natural predators to create more sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions to keeping plants healthy.
The importance of beneficial insects like Aphid Lions and Mealybug Destroyers cannot be overstated. They are the unsung heroes of the garden, working tirelessly to protect our plants and ensure a bountiful harvest. Want to learn more about these beneficial controls?
Check out the following articles to learn more:
Learn More about Aphids here.
Learn More about Mealybugs here.
Learn More about Aphid & Mealybug Predators here.


